(9778818威尼斯张学海)国际知名期刊《International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer》上近日发表了威尼斯官网郭会荣教授团队的论文——高压条件下CO2在水溶液中的热扩散研究(Soret effect on the diffusion of CO2 in aqueous solution under high-pressure)。
在CO2地质封存过程中,CO2注入地层后的溶解扩散除受浓度梯度的影响,还受到温度梯度的影响。温度较低的注入井附近和温度较高的地下岩层存在一定的温度梯度,这种由温度梯度引起的溶质扩散运动被称为热扩散现象。前人对水文地质领域的热扩散的研究尚属空白。郭会荣教授团队首次利用拉曼定量观测方法研究了地层压力下CO2在水溶液中的热扩散过程,定量获取了广阔温压条件下CO2在水中的热扩散系数。研究结果表明:不同深度条件下,温度梯度对二氧化碳的扩散迁移有着不同的影响:在温度压力较低的浅部地层(深度小于3000米),热扩散系数为正值,温度梯度趋向于将CO2驱动到温度较低的一侧(向上运移);当地层深度大于3000米时,热扩散系数为负值,温度梯度趋向于将CO2驱动到温度较高的一侧(向下运动)。该成果为研究地热梯度驱动下含水层中溶解气体的迁移提供了定量分析模型和参数。
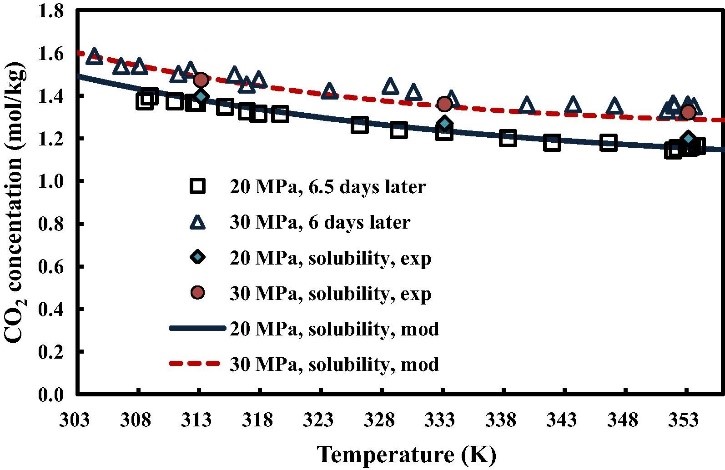
Fig. 1. Comparison of the steady state CO2 concentration profiles at 20 and 30 MPa, to the solubility measured by Guo et al. [14] (solubility, exp), and the solubility calculated from the model developed by Guo et al. [15] (solubility, mod).

Fig. 2. Soret coefficient of the CO2 in water as a function of the temperature and the pressure. The bold dashed line represents temperature-dependent soret coefficient under a typical geothermal gradients, assuming the surface temperature is around 293 K and the geothermal gradients are 30 K/km.
论文信息:
Soret effect on the diffusion of CO2 in aqueous solution under high-pressure
Huirong Guo*, Qian Zhou, Zhe Wang, Yiqi Huang
First published: 23 October 2017
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.10.058
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.10.058
